
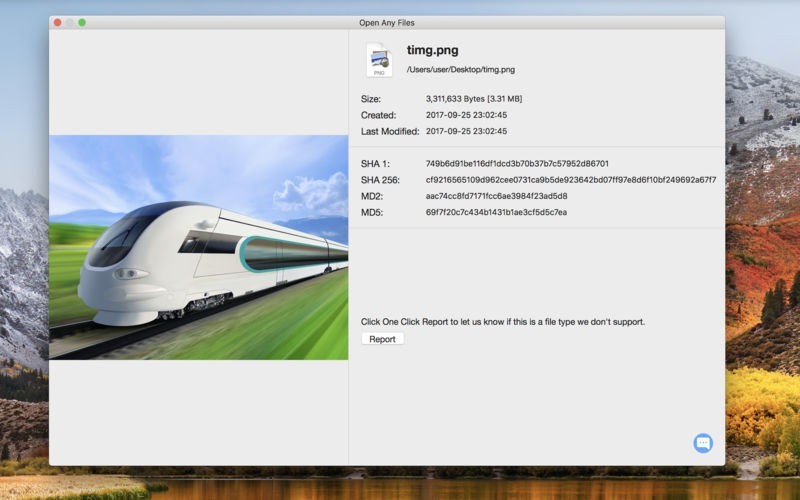
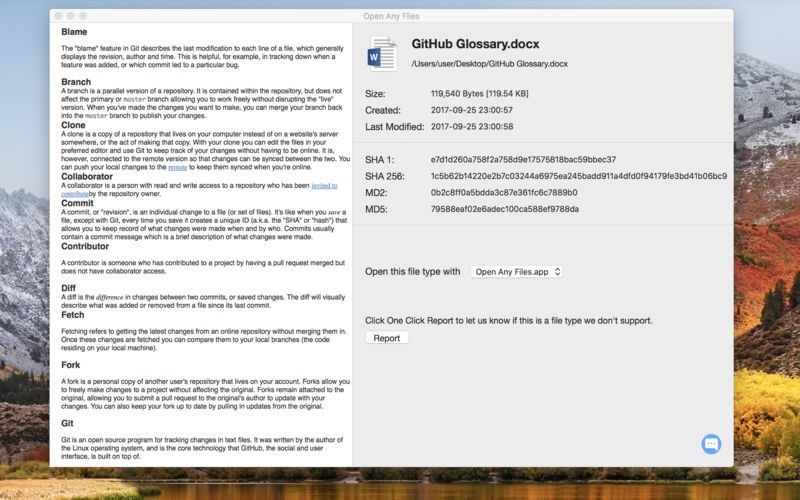
HTML is the universal standard markup language for web browsers. Markup languages control how data stored in files appear to end-users. HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. Non-Microsoft products that contain support for DOCX include: Because it stores data in a markup language (XML), DOCX has high interoperability with applications and browsers. DOCX is an XML-based file type capable of storing spreadsheets, charts, and various multimedia data in addition to documents. In 2008, Microsoft replaced DOC with DOCX (Office Open XML or OOXML) as the default Word file format. Although DOC is native to Microsoft Word, other common word processors such as Apple Pages and AbiWord can create, read, and edit DOC files. DOC and DOCXĭOC – short for document – is a Microsoft proprietary filename extension for storing documents in Microsoft Word Binary File Format. Currently, there are eight types you’re likely to encounter in the course of office document management. 8 Document File Types and ExtensionsĪlthough developers have used more than two dozen document filename extensions in the past, more than half of these have fallen out of use. With regard to documents, filename extensions typically tell users what kind of programs will be compatible with the file, whether it is a markup language for use in a web browser and whether it may have read-only functionality. As programs became more complex and operating systems multiplied, developers shifted towards using filename extensions to indicate associated programs or functions. Over time, developers began writing programs with multimedia functionality capable of handling a variety of data types. Filename extensions are a class of metadata, and they contain information about how data is stored in a file and how it is used.ĭevelopers originally used filename extensions to indicate catalog or index information to other users such as TXT for plain text, MUS for music, and GFX for graphics. What are Document File Types and Extensions?ĭocument file types or extensions – also called filename extensions – refer to the 2-4 letter suffixes appended to a filename after a period.
Some document file types are proprietary releases by developers such as Microsoft, some are open-source, and others are written in markup languages for rendering information in web browsers.Developers have used dozens of document file types in the history of electronic document storage but you’re likely to encounter fewer than ten of these in current use.Document file types and extensions are suffixes on filenames that tell users what kind of information to expect in a file and what kind of applications they can use to open a file.Locate and right-click the desired folder, then select Send to Desktop (create shortcut).Also note that copying a shortcut onto a flash drive will not work if you want to bring a file with you, you'll need to navigate to the actual location of the file and copy it to the flash drive. If you delete a shortcut, it will not delete the actual folder or the files it contains. Note that creating a shortcut does not create a duplicate copy of the folder it's simply a way to access the folder more quickly. A shortcut will have a small arrow in the lower-left corner of the icon.
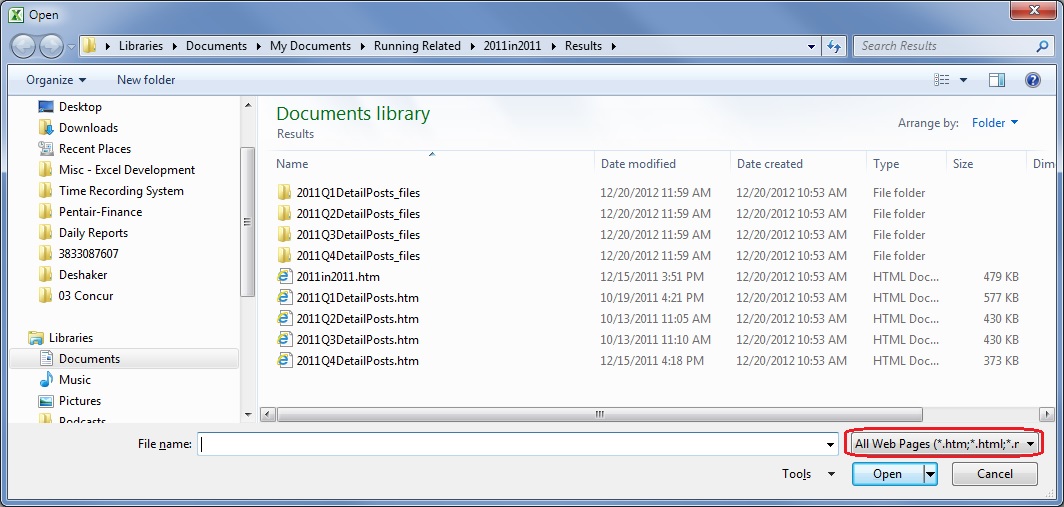
Instead of navigating to the file or folder each time you want to use it, you can simply double-click the shortcut to open it. If you have a file or folder you use frequently, you can save time by creating a shortcut on the desktop.
#Program that lets you open any file type how to#
In the next lesson, we'll talk about another important concept: how to find files on your computer that you can't easily locate. You'll start to feel more comfortable as you continue using your computer. If working with files and folders feels a little tricky right now, don't worry! Like anything else, working with files and folders is largely a matter of practice. We'll talk more about these in our lesson on Keyboard Shortcuts in Windows. Ctrl+A is an example of a keyboard shortcut.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
